Android Does My Text Have to Be Continuous or Can I Start New Thread
Writing custom platform-specific code
- Architectural overview: platform channels
- Platform channel data types support and codecs
- Example: Calling platform-specific Android, iOS, and Windows code using platform channels
- Step 1: Create a new app project
- Step 2: Create the Flutter platform client
- Step 3: Add an Android platform-specific implementation
- Step 4: Add an iOS platform-specific implementation
- Step 5: Add a Windows platform-specific implementation
- Typesafe platform channels using Pigeon
- Pigeon example
- Separate platform-specific code from UI code
- Publish platform-specific code as a package
- Custom channels and codecs
- Channels and platform threading
- Executing channel handlers on background threads
- Jumping to the UI thread in Android
- Jumping to the main thread in iOS
This guide describes how to write custom platform-specific code. Some platform-specific functionality is available through existing packages; see using packages.
Flutter uses a flexible system that allows you to call platform-specific APIs in a language that works directly with those APIs:
- Kotlin or Java on Android
- Swift or Objective-C on iOS
- C++ on Windows
- Objective-C on macOS
- C on Linux
Flutter's builtin platform-specific API support doesn't rely on code generation, but rather on a flexible message passing style. Alternatively, you can use the Pigeon package for sending structured typesafe messages with code generation:
-
The Flutter portion of the app sends messages to its host, the non-Dart portion of the app, over a platform channel.
-
The host listens on the platform channel, and receives the message. It then calls into any number of platform-specific APIs—using the native programming language—and sends a response back to the client, the Flutter portion of the app.
Architectural overview: platform channels
Messages are passed between the client (UI) and host (platform) using platform channels as illustrated in this diagram:
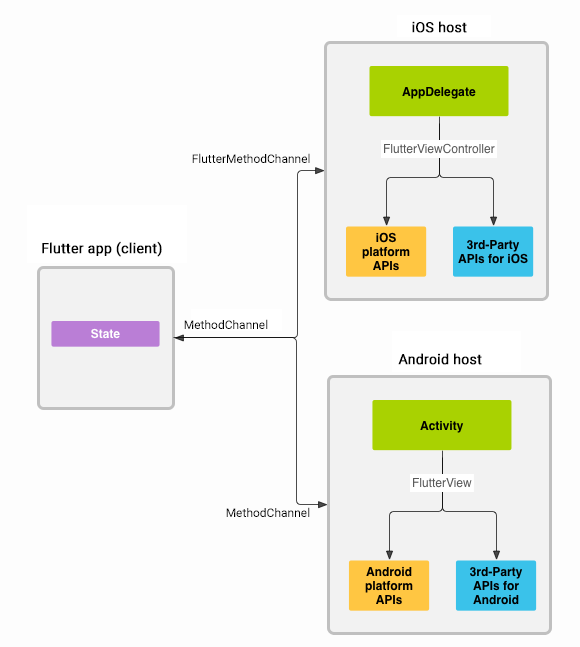
Messages and responses are passed asynchronously, to ensure the user interface remains responsive.
On the client side, MethodChannel enables sending messages that correspond to method calls. On the platform side, MethodChannel on Android (MethodChannelAndroid) and FlutterMethodChannel on iOS (MethodChanneliOS) enable receiving method calls and sending back a result. These classes allow you to develop a platform plugin with very little 'boilerplate' code.
Platform channel data types support and codecs
The standard platform channels use a standard message codec that supports efficient binary serialization of simple JSON-like values, such as booleans, numbers, Strings, byte buffers, and Lists and Maps of these (see StandardMessageCodec for details). The serialization and deserialization of these values to and from messages happens automatically when you send and receive values.
The following table shows how Dart values are received on the platform side and vice versa:
| Dart | Java |
|---|---|
| null | null |
| bool | java.lang.Boolean |
| int | java.lang.Integer |
| int, if 32 bits not enough | java.lang.Long |
| double | java.lang.Double |
| String | java.lang.String |
| Uint8List | byte[] |
| Int32List | int[] |
| Int64List | long[] |
| Float32List | float[] |
| Float64List | double[] |
| List | java.util.ArrayList |
| Map | java.util.HashMap |
| Dart | Kotlin |
|---|---|
| null | null |
| bool | Boolean |
| int | Int |
| int, if 32 bits not enough | Long |
| double | Double |
| String | String |
| Uint8List | ByteArray |
| Int32List | IntArray |
| Int64List | LongArray |
| Float32List | FloatArray |
| Float64List | DoubleArray |
| List | List |
| Map | HashMap |
| Dart | Objective-C |
|---|---|
| null | nil (NSNull when nested) |
| bool | NSNumber numberWithBool: |
| int | NSNumber numberWithInt: |
| int, if 32 bits not enough | NSNumber numberWithLong: |
| double | NSNumber numberWithDouble: |
| String | NSString |
| Uint8List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithBytes: |
| Int32List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithInt32: |
| Int64List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithInt64: |
| Float32List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithFloat32: |
| Float64List | FlutterStandardTypedData typedDataWithFloat64: |
| List | NSArray |
| Map | NSDictionary |
| Dart | Swift |
|---|---|
| null | nil |
| bool | NSNumber(value: Bool) |
| int | NSNumber(value: Int32) |
| int, if 32 bits not enough | NSNumber(value: Int) |
| double | NSNumber(value: Double) |
| String | String |
| Uint8List | FlutterStandardTypedData(bytes: Data) |
| Int32List | FlutterStandardTypedData(int32: Data) |
| Int64List | FlutterStandardTypedData(int64: Data) |
| Float32List | FlutterStandardTypedData(float32: Data) |
| Float64List | FlutterStandardTypedData(float64: Data) |
| List | Array |
| Map | Dictionary |
| Dart | C++ |
|---|---|
| null | EncodableValue() |
| bool | EncodableValue(bool) |
| int | EncodableValue(int32_t) |
| int, if 32 bits not enough | EncodableValue(int64_t) |
| double | EncodableValue(double) |
| String | EncodableValue(std::string) |
| Uint8List | EncodableValue(std::vector |
| Int32List | EncodableValue(std::vector |
| Int64List | EncodableValue(std::vector |
| Float32List | EncodableValue(std::vector |
| Float64List | EncodableValue(std::vector |
| List | EncodableValue(std::vector |
| Map | EncodableValue(std::map<EncodableValue, EncodableValue>) |
| Dart | C (GObject) |
|---|---|
| null | FlValue() |
| bool | FlValue(bool) |
| int | FlValue(int62_t) |
| double | FlValue(double) |
| String | FlValue(gchar*) |
| Uint8List | FlValue(uint8_t*) |
| Int32List | FlValue(int32_t*) |
| Int64List | FlValue(int64_t*) |
| Float32List | FlValue(float*) |
| Float64List | FlValue(double*) |
| List | FlValue(FlValue) |
| Map | FlValue(FlValue, FlValue) |
Example: Calling platform-specific Android, iOS, and Windows code using platform channels
The following code demonstrates how to call a platform-specific API to retrieve and display the current battery level. It uses the Android BatteryManager API, the iOS device.batteryLevel API, and the Windows GetSystemPowerStatus API with a single platform message, getBatteryLevel().
The example adds the platform-specific code inside the main app itself. If you want to reuse the platform-specific code for multiple apps, the project creation step is slightly different (see developing packages), but the platform channel code is still written in the same way.
Step 1: Create a new app project
Start by creating a new app:
- In a terminal run:
flutter create batterylevel
By default, our template supports writing Android code using Kotlin, or iOS code using Swift. To use Java or Objective-C, use the -i and/or -a flags:
- In a terminal run:
flutter create -i objc -a java batterylevel
Step 2: Create the Flutter platform client
The app's State class holds the current app state. Extend that to hold the current battery state.
First, construct the channel. Use a MethodChannel with a single platform method that returns the battery level.
The client and host sides of a channel are connected through a channel name passed in the channel constructor. All channel names used in a single app must be unique; prefix the channel name with a unique 'domain prefix', for example: samples.flutter.dev/battery.
import 'dart:async'; import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; import 'package:flutter/services.dart'; class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> { static const platform = MethodChannel('samples.flutter.dev/battery'); // Get battery level. Next, invoke a method on the method channel, specifying the concrete method to call using the String identifier getBatteryLevel. The call might fail—for example, if the platform doesn't support the platform API (such as when running in a simulator), so wrap the invokeMethod call in a try-catch statement.
Use the returned result to update the user interface state in _batteryLevel inside setState.
// Get battery level. String _batteryLevel = 'Unknown battery level.'; Future<void> _getBatteryLevel() async { String batteryLevel; try { final int result = await platform.invokeMethod('getBatteryLevel'); batteryLevel = 'Battery level at $result % .'; } on PlatformException catch (e) { batteryLevel = "Failed to get battery level: '${e.message}'."; } setState(() { _batteryLevel = batteryLevel; }); } Finally, replace the build method from the template to contain a small user interface that displays the battery state in a string, and a button for refreshing the value.
@override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Material( child: Center( child: Column( mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly, children: [ ElevatedButton( onPressed: _getBatteryLevel, child: const Text('Get Battery Level'), ), Text(_batteryLevel), ], ), ), ); } Step 3: Add an Android platform-specific implementation
Start by opening the Android host portion of your Flutter app in Android Studio:
-
Start Android Studio
-
Select the menu item File > Open…
-
Navigate to the directory holding your Flutter app, and select the android folder inside it. Click OK.
-
Open the file
MainActivity.ktlocated in the kotlin folder in the Project view.
Inside the configureFlutterEngine() method, create a MethodChannel and call setMethodCallHandler(). Make sure to use the same channel name as was used on the Flutter client side.
import androidx.annotation.NonNull import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel class MainActivity : FlutterActivity () { private val CHANNEL = "samples.flutter.dev/battery" override fun configureFlutterEngine ( @NonNull flutterEngine : FlutterEngine ) { super . configureFlutterEngine ( flutterEngine ) MethodChannel ( flutterEngine . dartExecutor . binaryMessenger , CHANNEL ). setMethodCallHandler { call , result -> // This method is invoked on the main thread. // TODO } } } Add the Android Kotlin code that uses the Android battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native Android app.
First, add the needed imports at the top of the file:
import android.content.Context import android.content.ContextWrapper import android.content.Intent import android.content.IntentFilter import android.os.BatteryManager import android.os.Build.VERSION import android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES Next, add the following method in the MainActivity class, below the configureFlutterEngine() method:
private fun getBatteryLevel (): Int { val batteryLevel : Int if ( VERSION . SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES . LOLLIPOP ) { val batteryManager = getSystemService ( Context . BATTERY_SERVICE ) as BatteryManager batteryLevel = batteryManager . getIntProperty ( BatteryManager . BATTERY_PROPERTY_CAPACITY ) } else { val intent = ContextWrapper ( applicationContext ). registerReceiver ( null , IntentFilter ( Intent . ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED )) batteryLevel = intent !! . getIntExtra ( BatteryManager . EXTRA_LEVEL , - 1 ) * 100 / intent . getIntExtra ( BatteryManager . EXTRA_SCALE , - 1 ) } return batteryLevel } Finally, complete the setMethodCallHandler() method added earlier. You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel(), so test for that in the call argument. The implementation of this platform method calls the Android code written in the previous step, and returns a response for both the success and error cases using the result argument. If an unknown method is called, report that instead.
Remove the following code:
MethodChannel ( flutterEngine . dartExecutor . binaryMessenger , CHANNEL ). setMethodCallHandler { call , result -> // This method is invoked on the main thread. // TODO } And replace with the following:
MethodChannel ( flutterEngine . dartExecutor . binaryMessenger , CHANNEL ). setMethodCallHandler { // This method is invoked on the main thread. call , result -> if ( call . method == "getBatteryLevel" ) { val batteryLevel = getBatteryLevel () if ( batteryLevel != - 1 ) { result . success ( batteryLevel ) } else { result . error ( "UNAVAILABLE" , "Battery level not available." , null ) } } else { result . notImplemented () } } Start by opening the Android host portion of your Flutter app in Android Studio:
-
Start Android Studio
-
Select the menu item File > Open…
-
Navigate to the directory holding your Flutter app, and select the android folder inside it. Click OK.
-
Open the
MainActivity.javafile located in the java folder in the Project view.
Next, create a MethodChannel and set a MethodCallHandler inside the configureFlutterEngine() method. Make sure to use the same channel name as was used on the Flutter client side.
import androidx.annotation.NonNull ; import io.flutter.embedding.android.FlutterActivity ; import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine ; import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel ; public class MainActivity extends FlutterActivity { private static final String CHANNEL = "samples.flutter.dev/battery" ; @Override public void configureFlutterEngine ( @NonNull FlutterEngine flutterEngine ) { super . configureFlutterEngine ( flutterEngine ); new MethodChannel ( flutterEngine . getDartExecutor (). getBinaryMessenger (), CHANNEL ) . setMethodCallHandler ( ( call , result ) -> { // This method is invoked on the main thread. // TODO } ); } } Add the Android Java code that uses the Android battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native Android app.
First, add the needed imports at the top of the file:
import android.content.ContextWrapper ; import android.content.Intent ; import android.content.IntentFilter ; import android.os.BatteryManager ; import android.os.Build.VERSION ; import android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES ; import android.os.Bundle ; Then add the following as a new method in the activity class, below the configureFlutterEngine() method:
private int getBatteryLevel () { int batteryLevel = - 1 ; if ( VERSION . SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES . LOLLIPOP ) { BatteryManager batteryManager = ( BatteryManager ) getSystemService ( BATTERY_SERVICE ); batteryLevel = batteryManager . getIntProperty ( BatteryManager . BATTERY_PROPERTY_CAPACITY ); } else { Intent intent = new ContextWrapper ( getApplicationContext ()). registerReceiver ( null , new IntentFilter ( Intent . ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED )); batteryLevel = ( intent . getIntExtra ( BatteryManager . EXTRA_LEVEL , - 1 ) * 100 ) / intent . getIntExtra ( BatteryManager . EXTRA_SCALE , - 1 ); } return batteryLevel ; } Finally, complete the setMethodCallHandler() method added earlier. You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel(), so test for that in the call argument. The implementation of this platform method calls the Android code written in the previous step, and returns a response for both the success and error cases using the result argument. If an unknown method is called, report that instead.
Remove the following code:
( call , result ) -> { // This method is invoked on the main thread. // TODO } And replace with the following:
( call , result ) -> { // This method is invoked on the main thread. if ( call . method . equals ( "getBatteryLevel" )) { int batteryLevel = getBatteryLevel (); if ( batteryLevel != - 1 ) { result . success ( batteryLevel ); } else { result . error ( "UNAVAILABLE" , "Battery level not available." , null ); } } else { result . notImplemented (); } } You should now be able to run the app on Android. If using the Android Emulator, set the battery level in the Extended Controls panel accessible from the … button in the toolbar.
Step 4: Add an iOS platform-specific implementation
Start by opening the iOS host portion of your Flutter app in Xcode:
-
Start Xcode.
-
Select the menu item File > Open….
-
Navigate to the directory holding your Flutter app, and select the ios folder inside it. Click OK.
Add support for Swift in the standard template setup that uses Objective-C:
-
Expand Runner > Runner in the Project navigator.
-
Open the file
AppDelegate.swiftlocated under Runner > Runner in the Project navigator.
Override the application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: function and create a FlutterMethodChannel tied to the channel name samples.flutter.dev/battery:
@UIApplicationMain @objc class AppDelegate : FlutterAppDelegate { override func application ( _ application : UIApplication , didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions : [ UIApplication . LaunchOptionsKey : Any ]?) -> Bool { let controller : FlutterViewController = window ? . rootViewController as! FlutterViewController let batteryChannel = FlutterMethodChannel ( name : "samples.flutter.dev/battery" , binaryMessenger : controller . binaryMessenger ) batteryChannel . setMethodCallHandler ({ ( call : FlutterMethodCall , result : @escaping FlutterResult ) -> Void in // This method is invoked on the UI thread. // Handle battery messages. }) GeneratedPluginRegistrant . register ( with : self ) return super . application ( application , didFinishLaunchingWithOptions : launchOptions ) } } Next, add the iOS Swift code that uses the iOS battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native iOS app.
Add the following as a new method at the bottom of AppDelegate.swift:
private func receiveBatteryLevel ( result : FlutterResult ) { let device = UIDevice . current device . isBatteryMonitoringEnabled = true if device . batteryState == UIDevice . BatteryState . unknown { result ( FlutterError ( code : "UNAVAILABLE" , message : "Battery level not available." , details : nil )) } else { result ( Int ( device . batteryLevel * 100 )) } } Finally, complete the setMethodCallHandler() method added earlier. You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel(), so test for that in the call argument. The implementation of this platform method calls the iOS code written in the previous step. If an unknown method is called, report that instead.
batteryChannel . setMethodCallHandler ({ [ weak self ] ( call : FlutterMethodCall , result : FlutterResult ) -> Void in // This method is invoked on the UI thread. guard call . method == "getBatteryLevel" else { result ( FlutterMethodNotImplemented ) return } self ? . receiveBatteryLevel ( result : result ) }) Start by opening the iOS host portion of the Flutter app in Xcode:
-
Start Xcode.
-
Select the menu item File > Open….
-
Navigate to the directory holding your Flutter app, and select the ios folder inside it. Click OK.
-
Make sure the Xcode projects builds without errors.
-
Open the file
AppDelegate.m, located under Runner > Runner in the Project navigator.
Create a FlutterMethodChannel and add a handler inside the application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions: method. Make sure to use the same channel name as was used on the Flutter client side.
#import <Flutter/Flutter.h> #import "GeneratedPluginRegistrant.h" @implementation AppDelegate - ( BOOL ) application :( UIApplication * ) application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions :( NSDictionary * ) launchOptions { FlutterViewController * controller = ( FlutterViewController * ) self . window . rootViewController ; FlutterMethodChannel * batteryChannel = [ FlutterMethodChannel methodChannelWithName: @"samples.flutter.dev/battery" binaryMessenger: controller . binaryMessenger ]; [ batteryChannel setMethodCallHandler : ^ ( FlutterMethodCall * call , FlutterResult result ) { // This method is invoked on the UI thread. // TODO }]; [ GeneratedPluginRegistrant registerWithRegistry : self ]; return [ super application : application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions : launchOptions ]; } Next, add the iOS ObjectiveC code that uses the iOS battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native iOS app.
Add the following method in the AppDelegate class, just before @end:
- ( int ) getBatteryLevel { UIDevice * device = UIDevice . currentDevice ; device . batteryMonitoringEnabled = YES ; if ( device . batteryState == UIDeviceBatteryStateUnknown ) { return - 1 ; } else { return ( int )( device . batteryLevel * 100 ); } } Finally, complete the setMethodCallHandler() method added earlier. You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel(), so test for that in the call argument. The implementation of this platform method calls the iOS code written in the previous step, and returns a response for both the success and error cases using the result argument. If an unknown method is called, report that instead.
__weak typeof ( self ) weakSelf = self ; [ batteryChannel setMethodCallHandler : ^ ( FlutterMethodCall * call , FlutterResult result ) { // This method is invoked on the UI thread. if ([ @"getBatteryLevel" isEqualToString : call . method ]) { int batteryLevel = [ weakSelf getBatteryLevel ]; if ( batteryLevel == - 1 ) { result ([ FlutterError errorWithCode : @"UNAVAILABLE" message: @"Battery level not available." details: nil ]); } else { result ( @ ( batteryLevel )); } } else { result ( FlutterMethodNotImplemented ); } }]; You should now be able to run the app on iOS. If using the iOS Simulator, note that it doesn't support battery APIs, and the app displays 'Battery level not available'.
Step 5: Add a Windows platform-specific implementation
Start by opening the Windows host portion of your Flutter app in Visual Studio:
-
Run
flutter build windowsin your project directory once to generate the Visual Studio solution file. -
Start Visual Studio.
-
Select Open a project or solution.
-
Navigate to the directory holding your Flutter app, then into the build folder, then the windows folder, then select the
batterylevel.slnfile. Click Open.
Add the C++ implementation of the platform channel method:
-
Expand batterylevel > Source Files in the Solution Explorer.
-
Open the file
flutter_window.cpp.
First, add the necessary includes to the top of the file, just after #include "flutter_window.h":
#include <flutter/event_channel.h> #include <flutter/event_sink.h> #include <flutter/event_stream_handler_functions.h> #include <flutter/method_channel.h> #include <flutter/standard_method_codec.h> #include <windows.h> #include <memory> Edit the FlutterWindow::OnCreate method and create a flutter::MethodChannel tied to the channel name samples.flutter.dev/battery:
bool FlutterWindow :: OnCreate () { // ... RegisterPlugins ( flutter_controller_ -> engine ()); flutter :: MethodChannel <> channel ( flutter_controller_ -> engine () -> messenger (), "samples.flutter.dev/battery" , & flutter :: StandardMethodCodec :: GetInstance ()); channel . SetMethodCallHandler ( []( const flutter :: MethodCall <>& call , std :: unique_ptr < flutter :: MethodResult <>> result ) { // TODO }); SetChildContent ( flutter_controller_ -> view () -> GetNativeWindow ()); return true ; } Next, add the C++ code that uses the Windows battery APIs to retrieve the battery level. This code is exactly the same as you would write in a native Windows application.
Add the following as a new function at the top of flutter_window.cpp just after the #include section:
static int GetBatteryLevel () { SYSTEM_POWER_STATUS status ; if ( GetSystemPowerStatus ( & status ) == 0 || status . BatteryLifePercent == 255 ) { return - 1 ; } return status . BatteryLifePercent ; } Finally, complete the setMethodCallHandler() method added earlier. You need to handle a single platform method, getBatteryLevel(), so test for that in the call argument. The implementation of this platform method calls the Windows code written in the previous step. If an unknown method is called, report that instead.
Remove the following code:
channel . SetMethodCallHandler ( []( const flutter :: MethodCall <>& call , std :: unique_ptr < flutter :: MethodResult <>> result ) { // TODO }); And replace with the following:
channel . SetMethodCallHandler ( []( const flutter :: MethodCall <>& call , std :: unique_ptr < flutter :: MethodResult <>> result ) { if ( call . method_name () == "getBatteryLevel" ) { int battery_level = GetBatteryLevel (); if ( battery_level != - 1 ) { result -> Success ( battery_level ); } else { result -> Error ( "UNAVAILABLE" , "Battery level not available." ); } } else { result -> NotImplemented (); } }); You should now be able to run the application on Windows. If your device doesn't have a battery, it displays 'Battery level not available'.
Typesafe platform channels using Pigeon
The previous example uses MethodChannel to communicate between the host and client, which isn't typesafe. Calling and receiving messages depends on the host and client declaring the same arguments and datatypes in order for messages to work. You can use the Pigeon package as an alternative to MethodChannel to generate code that sends messages in a structured, typesafe manner.
With Pigeon, the messaging protocol is defined in a subset of Dart that then generates messaging code for Android or iOS. You can find a more complete example and more information on the pigeon page on pub.dev.
Using Pigeon eliminates the need to match strings between host and client for the names and datatypes of messages. It supports: nested classes, grouping messages into APIs, generation of asynchronous wrapper code and sending messages in either direction. The generated code is readable and guarantees there are no conflicts between multiple clients of different versions. Supported languages are Objective-C, Java, Kotlin, and Swift (with Objective-C interop).
Pigeon example
Pigeon file:
import 'package:pigeon/pigeon.dart'; class SearchRequest { String query = ''; } class SearchReply { String result = ''; } @HostApi() abstract class Api { Future search(SearchRequest request); } Dart usage:
import 'generated_pigeon.dart'; Future<void> onClick() async { SearchRequest request = SearchRequest()..query = 'test'; Api api = SomeApi(); SearchReply reply = await api.search(request); print('reply: ${reply.result}'); } Separate platform-specific code from UI code
If you expect to use your platform-specific code in multiple Flutter apps, you might consider separating the code into a platform plugin located in a directory outside your main application. See developing packages for details.
Publish platform-specific code as a package
To share your platform-specific code with other developers in the Flutter ecosystem, see publishing packages.
Custom channels and codecs
Besides the above mentioned MethodChannel, you can also use the more basic BasicMessageChannel, which supports basic, asynchronous message passing using a custom message codec. You can also use the specialized BinaryCodec, StringCodec, and JSONMessageCodec classes, or create your own codec.
You might also check out an example of a custom codec in the cloud_firestore plugin, which is able to serialize and deserialize many more types than the default types.
Channels and platform threading
When invoking channels on the platform side destined for Flutter, invoke them on the platform's main thread. When invoking channels in Flutter destined for the platform side, invoke on the root Isolate. The platform side's handlers can execute on the platform's main thread or they can execute on a background thread if using a Task Queue. You can invoke the platform side handlers asynchronously and on any thread when the Task Queue API is available; otherwise, they must be invoked on the platform thread.
Executing channel handlers on background threads
In order for a channel's platform side handler to execute on a background thread, you must use the Task Queue API. Currently this feature is only supported on iOS and Android.
In Java:
@Override public void onAttachedToEngine ( @NonNull FlutterPluginBinding binding ) { BinaryMessenger messenger = binding . getBinaryMessenger (); BinaryMessenger . TaskQueue taskQueue = messenger . makeBackgroundTaskQueue (); channel = new MethodChannel ( messenger , "com.example.foo" , StandardMethodCodec . INSTANCE , taskQueue ); channel . setMethodCallHandler ( this ); } In Kotlin:
override fun onAttachedToEngine ( @NonNull flutterPluginBinding : FlutterPlugin . FlutterPluginBinding ) { val taskQueue = flutterPluginBinding . binaryMessenger . makeBackgroundTaskQueue () channel = MethodChannel ( flutterPluginBinding . binaryMessenger , "com.example.foo" , StandardMethodCodec . INSTANCE , taskQueue ) channel . setMethodCallHandler ( this ) } In Swift:
public static func register ( with registrar : FlutterPluginRegistrar ) { let taskQueue = registrar . messenger . makeBackgroundTaskQueue () let channel = FlutterMethodChannel ( name : "com.example.foo" , binaryMessenger : registrar . messenger (), codec : FlutterStandardMethodCodec . sharedInstance , taskQueue : taskQueue ) let instance = MyPlugin () registrar . addMethodCallDelegate ( instance , channel : channel ) } In Objective-C:
+ ( void ) registerWithRegistrar :( NSObject < FlutterPluginRegistrar >* ) registrar { NSObject < FlutterTaskQueue >* taskQueue = [[ registrar messenger ] makeBackgroundTaskQueue ]; FlutterMethodChannel * channel = [ FlutterMethodChannel methodChannelWithName : @"com.example.foo" binaryMessenger: [ registrar messenger ] codec: [ FlutterStandardMethodCodec sharedInstance ] taskQueue: taskQueue ]; MyPlugin * instance = [[ MyPlugin alloc ] init ]; [ registrar addMethodCallDelegate : instance channel : channel ]; } Jumping to the UI thread in Android
To comply with channels' UI thread requirement, you might need to jump from a background thread to Android's UI thread to execute a channel method. In Android, you can accomplish this by post()ing a Runnable to Android's UI thread Looper, which causes the Runnable to execute on the main thread at the next opportunity.
In Java:
new Handler ( Looper . getMainLooper ()). post ( new Runnable () { @Override public void run () { // Call the desired channel message here. } }); In Kotlin:
Handler ( Looper . getMainLooper ()). post { // Call the desired channel message here. } Jumping to the main thread in iOS
To comply with channel's main thread requirement, you might need to jump from a background thread to iOS's main thread to execute a channel method. Youc an accomplish this in iOS by executing a block on the main dispatch queue:
In Objective-C:
dispatch_async ( dispatch_get_main_queue (), ^ { // Call the desired channel message here. }); In Swift:
DispatchQueue . main . async { // Call the desired channel message here. } scottsiondonsen64.blogspot.com
Source: https://docs.flutter.dev/development/platform-integration/platform-channels
Post a Comment for "Android Does My Text Have to Be Continuous or Can I Start New Thread"